SEO cannibalization occurs when multiple pages on your site compete for the same keyword. AND the same search intent. Result: unstable rankings, lost backlinks, and stagnant traffic.
Most effective solution: consolidate content with 301 redirects (Backlinko got +466% clicks). Prevention: keyword mapping (1 keyword = 1 page) + quarterly audits with Google Search Console.
Are your pages competing against each other instead of competitors? If you've noticed unstable rankings, traffic that isn't growing despite quality content, or the "wrong" page ranking for your main keywords, you may have a SEO problem. SEO cannibalization.
Keyword cannibalization is one of the most underrated SEO problems, yet it can silently sabotage months of work. The good news? It's solvable. Backlinko has documented a 466% increase in clicks after consolidating two articles that were competing for the same keywords (source).
In this comprehensive guide, you'll discover exactly what cannibalization is, how to identify it with free and paid tools, and the 6 most effective strategies to solve it once and for all.

What is Keyword Cannibalization?
SEO cannibalization occurs when two or more pages on the same site compete for the same keyword and the same search intent. It's not just about using the same keyword on different pages, but about creating content that answers the same user question.
Google's John Mueller described this phenomenon aptly: it's like a group of kids trying to be first in line, and eventually someone else gets ahead of everyone else. Your pages are hindering each other instead of working together to beat the competition.
The problem is never the keyword itself, but the’intent. If two pages try to answer the same question, Google doesn't know which one to show and often ends up penalizing both.
Cannibalization vs. Content Overlap vs. Duplicate Content
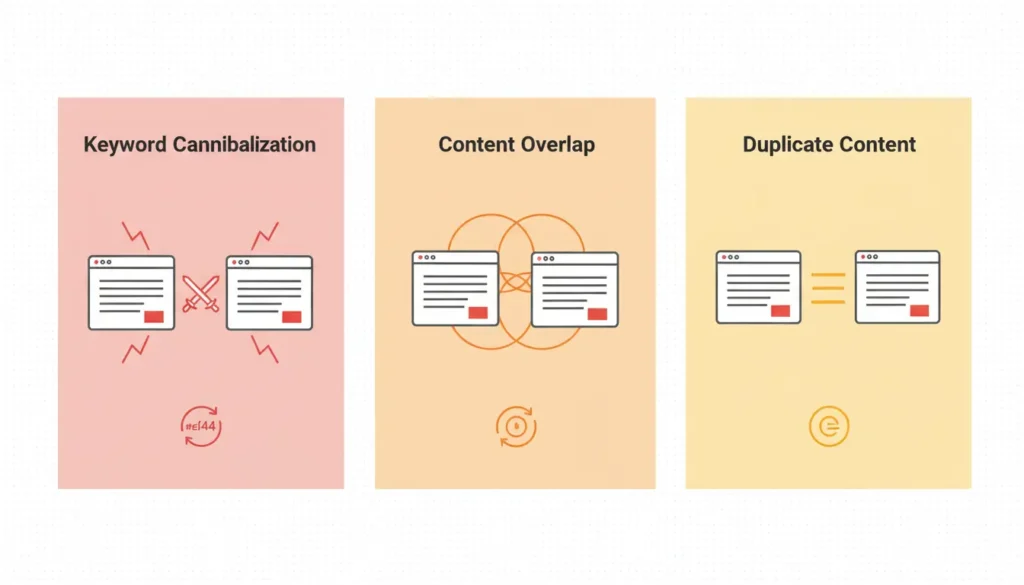
Before proceeding, it is essential to distinguish three often confused but substantially different problems:

| Type | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Keyword Cannibalization | Same keywords + same intent on the same site | 2 “best running shoes” guides, both for purchasing |
| Content Overlap | Same topic, different keywords, similar intent | “Content strategy” vs “Content marketing” vs “Content plan” |
| Duplicate Content | Identical or nearly identical text on multiple pages | Copied product page templates, duplicate city pages |
The fundamental difference lies in the’intentCannibalization refers to pages competing for the same user need, not simply pages mentioning the same words.
When Cannibalization is NOT a Problem
Not all keyword overlap situations are problematic. Cannibalization it's not a problem When:
- One page performs well and the others do not significantly interfere with its rankings
- Pages serve different intents: for example, an informational blog “How to choose running shoes” and a product page “Nike running shoes” can coexist
- Pages target different audiences: localized pages for different cities with the same service keyword
Practical example: For the query "Paris hotels," Google displays both informational guides and booking pages. If you have both types of content, there's no cannibalization because they serve different intents (informational vs. transactional).
Why Cannibalization Hurts SEO
When your site's pages compete with each other, the negative effects quickly add up. Here are the five main ones:
1. Dilutes Ranking Power
Instead of concentrating all the authority on a single strong page, you split it across multiple weak URLs. According to FirstPageSage's 2024 CTR study, the top two results on Google get almost 3 times more clicks compared to the third (source). Having two pages in positions 6 and 8 is much worse than having one in position 2.
2. It scatters backlinks
When other sites link to your similar content, the links become randomly distributed instead of reinforcing a single authoritative resource. If you get five links to one page and ten to another on the same topic, you could have concentrated all fifteen on one page, which would have ranked much higher.
3. Confuses Search Engines
Google struggles to determine which page is most relevant. The result? Unstable rankings, with pages constantly swapping positions. You might notice a page in position 5 on Monday and position 15 on Friday, for no apparent reason.
4. Waste your crawl budget
Googlebot spends time and resources crawling similar pages instead of discovering and indexing your new content. For sites with thousands of pages, this can become a serious problem.
5. Degrades User Experience
Users who encounter similar or repetitive content on your site lose trust in your brand. Bounce rates increase, engagement decreases, and these negative signals further impact rankings.
How to Identify SEO Cannibalization
Warning Signs
Before using specific tools, look for these typical symptoms:
- Rankings that fluctuate: pages that swap positions for the same query
- Low CTR despite good impressions
- Traffic divided between multiple URLs for the same query
- “Wrong” page that ranks: the commercial landing page is surpassed by an old blog post
Method 1: Google Search Console (Free)

Google Search Console is the ideal starting point because it provides real data directly from Google. Here's the step-by-step process:

- Log in to GSC and go to Performance → Search Results
- Scroll down to the list of queries and click on a keyword you want to analyze
- Switch to tab “Pages” (Pages)
- If they appear multiple URLs for the same query, there could be cannibalization
- Analyze clicks, impressions, CTR and average position for each URL
Pro tip: Use the "+ New" → "Query" filter to search for specific keywords. You can also use "contains" to analyze related keyword variations.
Method 2: Google's site: operator
A quick and free method: search directly on Google using the site operator:
site:yoursite.com "target keyword""If you see 2 or more pages with similar titles and descriptions, manually check for overlapping intent.
Method 3: Ahrefs Site Explorer
Ahrefs offers a more detailed view with historical data:
- Enter your domain into Site Explorer
- Go to Organic Keywords
- Filter by target keyword
- If multiple URLs rank for the same keyword, analyze their ranking history to see if they swap positions.
The advantage of Ahrefs is the ability to see the history: if you notice that two pages alternate in the same position over time, it's a clear sign of cannibalization.
Method 4: SEMrush Position Tracking
SEMrush has a dedicated report on cannibalization:
- Set up a Position Tracking project for your domain
- Add keywords to monitor
- Go to tab “Cannibalization”
- The report automatically shows: Affected keywords, Cannibal pages, Positions by date
SEMrush's Cannibalization Report is probably the most comprehensive and automated tool available, ideal for sites with many pages.
Method 5: Screaming Frog
For a more in-depth technical analysis:
- Crawl your site with Screaming Frog
- Export data from H1 and Title tags
- Find duplicate or very similar titles in a spreadsheet
This method reveals potential problems before they even show up in the rankings, allowing you to take preemptive action.
How to Fix Keyword Cannibalization
Once you've identified the problem, you have several treatment options. The choice depends on the specific situation.

Solution 1: Consolidation with 301 Redirect (Most Effective)
When to use it: Pages with the same intent, where one clearly performs better than the other.
Procedure:
- Identify the “winning” page (more backlinks, more traffic, better content)
- Integrate unique and valuable content from the secondary page into the winning page
- Set a 301 redirect from deleted page to merged page
- Update all internal links that pointed to the old page
- Remove URL from sitemap
📊 CASE STUDY: Backlinko
Backlinko had two competing articles for “SEO tools”: one was an extensive list, the other was more focused on free tools. After consolidating the content and implementing a 301 redirect, they recorded a 466% increase in clicks year over year. A simple procedure with extraordinary results (source).
📈 MY CASE STUDY: Woosa.com (+400% Organic Traffic)
I managed a complete SEO project for Woosa, an Italian mattress e-commerce site. During the initial audit, I identified: 7 pages that cannibalized key keywordsBuying guides, category pages, and blog posts all competed for “best mattress” and variants.
Intervention: I consolidated 4 pages into the main guide with 301 redirects, re-optimized 2 articles for specific long-tail keywords (“mattress for back pain,” “memory foam mattress vs. latex”), and implemented strategic internal linking to the pillar page.
Result: +400% organic traffic in 4 months, with the pillar page moving from position 12 to position 3 for “best mattress.” The consolidation also concentrated 23 referring domains into a single URL instead of being spread across seven.
Solution 2: Re-optimize for a Different Keyword
When to use it: Both pages are valuable and you don't want to delete either one.
Instead of deleting a page, change its target:
- Use tools keyword research to find an alternative keyword (preferably long-tail)
- Rewrite the subpage for the new target
- Differentiate the intent (e.g., from “best SEO tools” to “free SEO tools for beginners”)
- Update your title, H1, meta description and content accordingly
Solution 3: Canonical Tag
When to use it: Similar pages are needed for UX or technical reasons, but only one needs to rank.
Add the canonical tag to your subpage to tell Google which version to prefer:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://tuosito.com/pagina-principale/">Attention: Canonicalization isn't a solution for true cannibalization of different content. It only works for technical duplicates or minor variations of the same page.
Solution 4: De-indexing (noindex)
When to use it: The page is useful for users but does not have to rank.
Procedure with Yoast SEO: Edit Page → Yoast SEO → Advanced → “Allow search engines to show this page?” → No
This keeps the page accessible to users but removes it from search results, eliminating competition.
Solution 5: Strategic Internal Linking
When to use it: You want to strengthen one page over the others without eliminating them.
- Identify the main page you want to push
- Add internal links towards that page from the secondary pages
- Use descriptive anchor text with your target keyword
- Remove or edit internal links to subpages that use the same anchor text
Solution 6: De-optimization
When to use it: A secondary page ranks but shouldn't, and you don't want to delete it.
- Remove or edit the target keyword from the title and H1 of the subpage
- Replace with alternative or more generic keywords
- Add a prominent internal link to the main page
How to Prevent SEO Cannibalization
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some strategies to avoid future problems:
1. Keyword Mapping (1 Keyword = 1 Page)
Create a central document that maps each page on your site to its primary target keyword. Before creating new content, always check that the keyword isn't already assigned. A simple spreadsheet with columns: URL | Primary keyword | Secondary keywords | Intent | Status is sufficient.
2. Content Brief Before Writing
Each new piece of content should start with a brief that includes: target keyword (verified as non-duplicate), specific search intent, differentiation from existing content, and internal links to include.
3. Periodic Content Audits
Schedule quarterly audits for large sites, and biannually for smaller sites. Use GSC and SEO tools to monitor and identify overlaps before they become serious problems. Read my Technical SEO Audit Guide to learn more.
4. Communication between Teams
If you work with multiple teams (SEO, content, product), share keyword mapping and coordinate content creation. Many cases of cannibalization arise when different teams create similar content unknowingly.
5. Topic Cluster Structure
Organize content into thematic clusters: a central pillar page for the main topic, supporting articles covering related long-tail links, and clear internal linking from the periphery to the center. This structure naturally prevents cannibalization.
Tools to Identify Cannibalization
Here is a summary of the available tools:
| Instrument | Type | Pro | Against |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Free | Real Google data, completely free | Requires manual analysis |
| Ahrefs | Paid | Historical data, powerful Site Explorer | High cost |
| SEMrush | Paid | Automatic cannibalization report | Learning curve |
| Screaming Frog | Freemium | Complete technical audit | Only 500 free URLs |
| Adrian's Keyword Tool | Free | Keyword + intent analysis, no registration | Expanding functionality |
Try mine Free Keyword Research Tool to analyze your keywords and identify potential overlapping intent.
Conclusion
SEO cannibalization is a sneaky problem because you often don't notice it until it's already damaged your rankings. But now you have all the tools to identify and fix it.
Remember the key points:
- Cannibalization refers to pages competing for the same keyword. AND the same intent, not simply pages that mention the same words
- It's not always a problem: always check if the pages serve different intents
- Consolidation with 301 redirects is often the most effective solution
- Prevention is better than cure: implement keyword mapping and periodic audits.
If you notice signs of cannibalization on your site, don't wait. Every day that passes means you're losing traffic and conversions.
Concerned about cannibalization on your site? Contact me for a personalized SEO audit and discover how to unlock the true potential of your organic traffic.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is SEO cannibalization always bad?
No. If the pages serve different intents (e.g., informational vs. transactional) or if one page performs well without interference from the others, there's no real problem. Always check the intent before adjusting.
How do I know if I have a cannibalization problem?
Typical symptoms include unstable rankings (pages swapping positions), low CTR despite good impressions, and traffic split between multiple URLs for the same query. Use Google Search Console to check: if multiple pages rank for the same query with similar intent, you likely have a problem.
Should I delete cannibalizing pages?
Not necessarily. You can consolidate them with a 301 redirect, re-optimize them for different keywords, use the canonical tag, or strengthen the main page with strategic internal linking. The choice depends on the value of each page.
Does the canonical tag solve cannibalization?
Only partially. Canonicalization is effective for technical duplicates or minor variations, but it doesn't address true cannibalization of different content. Google can also ignore canonicalization if it deems the pages sufficiently different.
How long does it take to see results after resolving cannibalization?
It depends on the competitiveness of the keywords and the crawl rate of your site. Typically, initial improvements are visible within 2-4 weeks of resolution. Full results may take 2-3 months. Monitor your progress with GSC.



